The rise of smart home technology has transformed how we live, making daily tasks easier, safer, and more efficient through the use of advanced devices. From smart thermostats and security cameras to intelligent lighting systems, these innovations have promised a seamless home experience. However, the implementation of smart home apps is not without its challenges. While they offer numerous benefits, several flaws regarding device incompatibility and access issues, particularly those dependent on internet connectivity, can undermine their effectiveness.
The Allure of Smart Home Devices
Smart home devices are designed to automate various tasks and enhance home security. For example, smart thermostats can learn users’ habits, adjusting temperatures to maximise comfort and energy efficiency. Smart lighting can be controlled remotely, allowing users to set schedules or change the ambience of their homes with ease. Security cameras can monitor properties in real time, providing peace of mind whether at home or away.
The convenience these devices offer is undeniable. Centralised control through smart home apps allows users to manage multiple devices from their smartphones. Scheduling routines and receiving alerts for specific events can streamline daily life, making the proposed future of smarter, more efficient homes a reality.
The Flaws in Smart Home Apps
Despite the advantages, several significant flaws exist within the realm of smart home apps that can hinder user experience and device functionality.
Incompatibility Issues
One of the most pressing concerns is the incompatibility among devices. Many smart home products are created by different manufacturers, each with its own app and ecosystem. While some brands strive for universal compatibility, many devices remain isolated within their respective systems. This fragmentation complicates integration and often necessitates multiple apps, creating a cumbersome user experience.
Users may find themselves unable to connect devices from different brands due to varying protocols. For instance, a smart thermostat might work flawlessly with one brand of smart assistants but face challenges connecting with another. This lack of standardisation can prevent users from maximising the potential of their smart homes, often leading to frustration as they navigate multiple systems and interfaces.
Dependence on Internet Connectivity
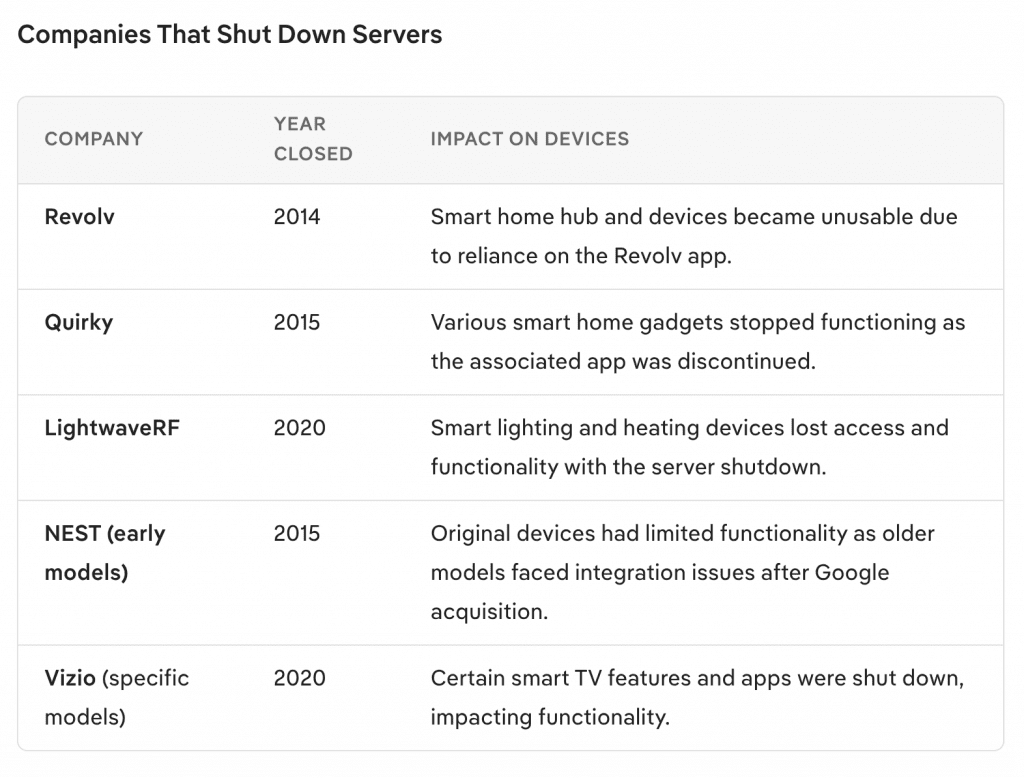
Another significant flaw is the dependence on consistent internet connectivity. Smart home devices rely on the internet for control and functionality, meaning that any service disruption can lead to severe limitations in device operation. For example, a power outage or internet failure could render smart security cameras ineffective, leaving homes vulnerable during the downtime.
Additionally, the reliance on cloud services for certain functionalities creates potential access issues. If a device is heavily reliant on cloud connectivity, users may face disruptions if the service goes down or if there are issues with their internet provider. This dependency can undermine the promise of a smarter home, as users lose access to controls they may have taken for granted.
Navigating the Smart Home Landscape
To navigate these challenges, consumers can opt for devices that prioritise compatibility by selecting products that adhere to well-established protocols. Researching devices that work well with existing systems can ensure a more integrated and seamless experience. Furthermore, developing a reliable internet infrastructure at home, including a robust router and potential mesh networks, can mitigate access issues.
In summary, while smart home devices hold the promise of revolutionising modern living, their flaws must be addressed for users to fully benefit from the connected lifestyle. By being informed and selective with their choices, consumers can overcome these obstacles to create a truly smart home that enhances their quality of life. Ultimately, the journey to a smarter home is a continuous evolution, promising innovation and enhanced living experiences with each advancement.